BDB650
Classical PM
Risk and Quality
Summary
Risk Management
Risk Management Processes
Project Quality Management
Project Quality Management - Processes
Risk Management
Risk Management
A risk is any uncertain event or condition that might affect your project
In other words: risk is anything that might change the outcome of a project activity
Risks are uncertain, they may or may not happen
Risks can be negative threats, or positive opportunities
Risk Management
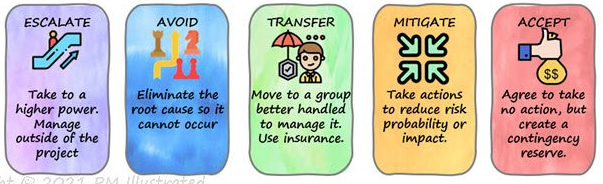
There are five basic ways to handle threats:
→ Avoid
→ Escalate
→ Mitigate
→ Transfer
→ Accept
Handling Threats
Risk Management
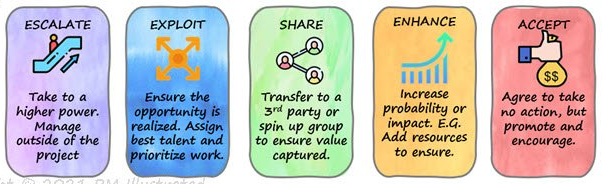
There are five ways to handle opportunities:
→ Escalate
→ Exploit
→ Enhance
→ Share
→ Accept
Handling Opportunities
Risk Management Processes
Risk Management Processes
The PMBOK delinates seven processes to handle risk
These steps help project managers identify, assess, respond to, and monitor risks
Risk Management Processes
1. Plan Risk Management
2. Identify Risk
3. Qualitative Risk Analysis
4. Quantitative Risk Analys
5. Plan Risk Responses
6. Implement R. Responses
7. Monitor Risk
Plan Risk Management
Purpose: Define how risk management will be conducted in the project
Key Activities:
→ Develop a Risk Management Plan
→ Define risk appetite, thresholds, and stakeholder risk tolerance
Identify Risk
Purpose: Identify potential risks that could affect the project
Key Activities:
→ Gather input from stakeholders, historical data, and expert judgment
→ Create a Risk Register, listing identified risks
Risk Register
| **ID** | **Risk Description** | **Likelihood** | **Impact** | **Risk Owner** | |------------|---------------------|--------------|----------|------------| | **01** | Data quality issues (incomplete, inaccurate, inconsistent data) | High | Medium | Data Engineer | | **02** | Non-compliance with data privacy regulations | Medium | High | Compliance Officer | | **03** | Model bias leading to incorrect insights and business decisions | Medium | High | Data Scientist | | **04** | Security vulnerabilities leading to data breaches | High | High | Security Engineer | | **05** | Unclear business requirements causing scope creep | Medium | Medium | Business Analyst | | **06** | Unexpected budget overruns due to cloud computing costs | Medium | Medium | Finance Manager |
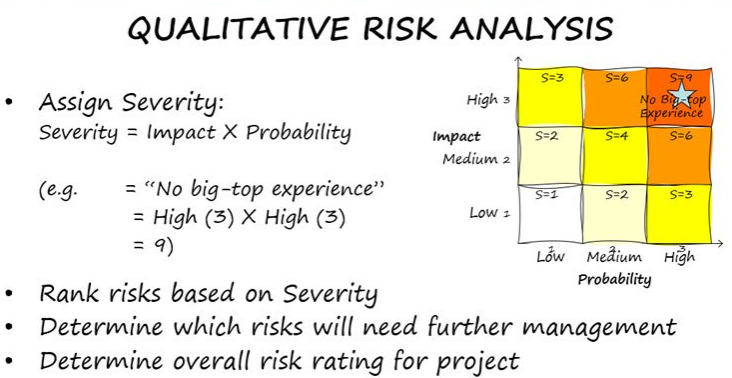
Qualitative Risk Analysis
Purpose: Prioritize risks based on their probability and impact
Key Activities:
→ Assess the likelihood and severity of each risk using Risk Probability and Impact Matrix
→ Identify high-priority risks
Qualitative Risk Analysis
Quantitative Risk Analysis
Purpose: Numerically analyze the impact of high-priority risks
Key Activities:
→ Use Monte Carlo Simulation, Decision Tree Analysis, Sensitivity Analysis, etc.
→ Evaluate risk exposure and calculate contingencies
Quantitative Risk Analysis
Purpose: Numerically analyze the impact of high-priority risks
Key Activities:
→ Use Monte Carlo Simulation, Decision Tree Analysis, Sensitivity Analysis, etc.
→ Evaluate risk exposure and calculate contingencies
Plan Risk Responses
Purpose: Develop strategies to address risks (both threats and opportunities)
Key Activities:
→ Select appropriate risk response strategies
→ Assign risk owners to implement responses
Implement Risk Responses
Purpose: Execute the planned risk responses
Key Activities:
→ Ensure risk responses are carried out as planned
→ Track implementation and make adjustments if needed
Monitor Risk
Purpose: Continuously track risks and evaluate effectiveness of responses
Key Activities:
→ Identify new risks that arise throughout the project
→Perform regular risk reviews and audits
Project Quality Management
Overview
Quality is “the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfill requirements"
Deliverables must meet the intended purpose and satisfy expectations from stakeholders
Deliverables must comply with industry regulations, organizational policies, and quality benchmarks
Cost of Quality
Quality in project does not come without a cost
Cost of Quality is a metric associated with Project Quality Management an encompases:
→ Prevention Costs
→ Appraisal Costs
→ Failure Costs
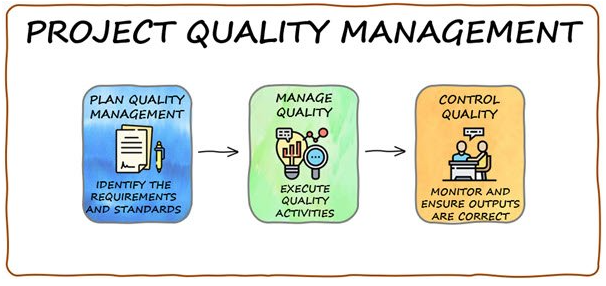
Project Quality Management
Processes
The PMI's PMBOK defines three key processes for Project Quality Management:
→ Plan Quality Management
→ Manage Quality
→ Control Quality
Project Quality Management
Processes
Project Quality Management
Processes
Plan Quality Management
Purpose: Define quality standards, quality objectives, and the criteria for success in the project
Key Activities:
→ Identify relevant quality standards
→Define quality metrics (e.g., defect rate, response time, reliability)
→Determine quality control and assurance processes and responsibilities
Manage Quality
Purpose: Ensure that the project processes are following the quality standards and requirements
Key Activities:
→ Conduct Quality Audits to check adherence to standards and identify improvements
→ Run tests and perform validation activities
→ Perform Process Analysis using tools like Root Cause Analysis, Fishbone Diagrams, and Flowcharts
Control Quality
Purpose: To inspect and verify that project deliverables meet the defined quality standards
Key Activities:
→ Conduct inspections, testing, and reviews of project deliverables
→ Identify Causes of unsatisfactory results