BDB650
Welcome and Introduction to Git
Summary
Introduction
Evaluation
git:
→ What is a git?
→ Installing git
→ Initializing, staging, and commiting
→ Status and logging
Introduction
About Myself
Brazilian, Canadian, and French
Father of two little honey badgers tasmanian devils beautiful children
Electrical Engineer by trade - ScrumMaster by option
+20 years of experience in Software Development
Teaching CAPSTONE Project courses since 2014
What we will Learn
Project Management:
→ What needs to be done?
→ How to get things done?
→ How to work effectively as a team?
→ How to communicate with stakeholders?
Modern Techniques
We will learn modern Project Management techniques applied to Software Development
An emphasis will be given to Agile
Within Agile, our focus will be on Scrum
Other frameworks, such as Kanban and CRISP-DM will also be covered
Classical Techniques
Classical Project Management techniques for:
→ scope, time, and cost
→ communications and stakeholder management
→ quality assurance and risk assessment
→ writing a project charter
Delivery Method
→ In-person lectures...
→ ... immediatly followed by workshops
→ Quizzes will be posted weekly
Technologies
→ Eventual recorded lectures: MS Teams
→ Reaching out: Teams or email
→ Announcements: Blackboard
→ Quizzes: Blackboard
→ Workshop submission: Github and Blackboard
Group work
Most workshops as well as the final assignment will consist of group work
Use Blackboard to form your groups
Each group will be assigned a Github repository
Some assignments will have both individual as well as group components
Evaluation
Types of Evaluation
10 Quizzes worth 1.5% each
10 Workshops worth 3.0% each
1 Final Assignment worth 10%
One midterm worth 20%
One final exam worth 25%
Quizzes
Individual work
Focus on theory
Posted and submitted on Blackboard weekly
Workshops
Individual and/or Groupwork
Focus on practical aspects
Posted on Blackboard, submitted on Blackboard or Github
Final Assignment
Groupwork
Compilation of workshops
Posted on Blackboard, submitted on Github
Includes a presentation component
Tests
Closed-book, pen-on-paper exams
Accommodations can be applied
Students must pass the overall course on average, and the tests on average!
What is git?
why do we need git?
How do you keep track of your files?
How does your team keep track of files?
Version Control Systems, VCS, make tracking and sharing development much more effective
They allow you to easily move into parallel realities as well as back and forward in time!
Version Control Systems
Version Control Systems allow for:
→ Keeping track of changes to files
→ Reverting changes
→ Tracking authorship
→ Parallel development
Git
There are other VCS, such as Subversion and Perforce
These systems are proprietary and require a centralized server
git was developed by the creator of Linux in 2005
By far the most popular VCS
It is free, as in free thinking
It does not require a centralized server
Installing git
Installing git
git can be installed for free in any OS
Afterwards, you can work with it via terminal or GUI integration
Installing git
After installing git, you should set up your username and email with:
git config --global user.name "NAME"
git config --global user.email "EMAIL"
Default Text Editor
After installing git, you should set up your default text editor with:
git config --global core.editor "code --wait"
git config --global core.editor "nano"
git config --global core.editor "vim"
Initializing, staging, and commiting
Basic commands
To initialize git in a folder, you simply type: git init
You can stage files with git add FILENAME
git add . stages all files in the current folder
You can commit all staged changes with:
git commit -m "MESSAGE"
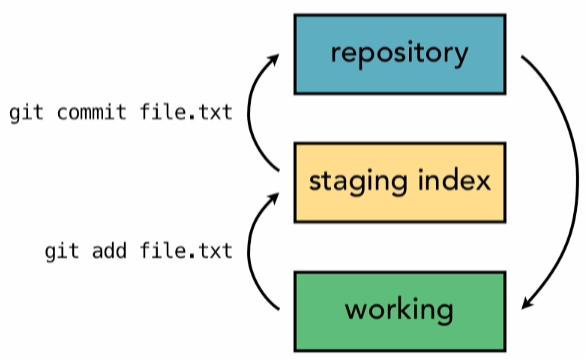
Three Trees
git tracks files using three trees:
Working Directory: Current files on the selected branch
Staging Area: Latest staged version of files
Repository: File versions in previous commits and different branches
See where things are at with: git status
Three Trees
Status and Logging
Git Status
At any point, you can check the current status of your repository with:
git status
This command shows:
→ which changes are untracked
→ which changes are staged
→ or if the directory is clean
Git log
You can check a list of previous commits with:
git log
This command will not show commits of unmerged branches
There are many options to format the log output