BDB650
Classical PM
PM Triangle: Cost and Time
Summary
Project Management Triangle
Time Management:
→ Dependencies
→ Gantt Charts
Cost Management
→ Estimation Techniques
→ Budgeting in SCRUM
Project Management Triangle
Introduction
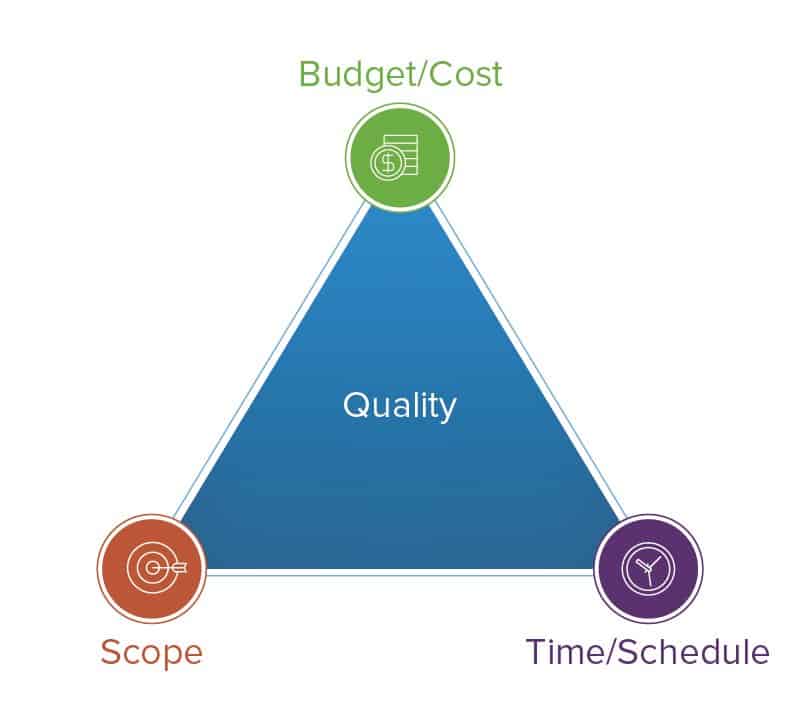
The quality of a project is dictated by three factors: scope, budget, and time
The combination of these factors is called: Project Management Triangle
Up to the manager to to achieve a proper trade-off
"Good, cheap, and fast. Pick two!"
Triple Constraint
Las class we discussed scope
This class will discuss time and cost
Time Management
Time Management
Time is often the variable that has the least amount of flexibility
Many projects have hard due dates: Christmas, Tax season, Competition, Contracts, etc.
Poor time management can also lead to extra costs
Time Management
After a scope has been determined, focus switches to the order in which activities are carried out
A number of tools have been developed over the years such as Gantt Charts and PERT Charts (Network Diagrams)
These tools help determine the order, dependencies, and how long a project will take
Dependencies
Dependencies
Dependencies (or relationships) dictate the logical sequencing of project activities
A clear understanding of dependencies is requried to build proper charts and diagrams
“Begin at the beginning," the King said, very gravely, "and go on till you come to the end: then stop.”
Dependencies Examples
Data Extraction depends on Data Availability
Data Cleaning depends on Raw Data being accessible
Exploratory Data Analysis depends on Cleaned and Transformed Data being accessible
Types of Dependencies
There are three types of dependencies:
→ Mandatory dependencies hard logic
→ Discretionary dependencies are agreed upon
→ External dependencies regards non-project activities
Gantt Charts
Gantt Charts
List project activities vs their start and finish dates
The Critical Path determines the earliest completion of a project
The more activities are in this path, the harder it is to make a proper prediction
Gantt Chart Example 1
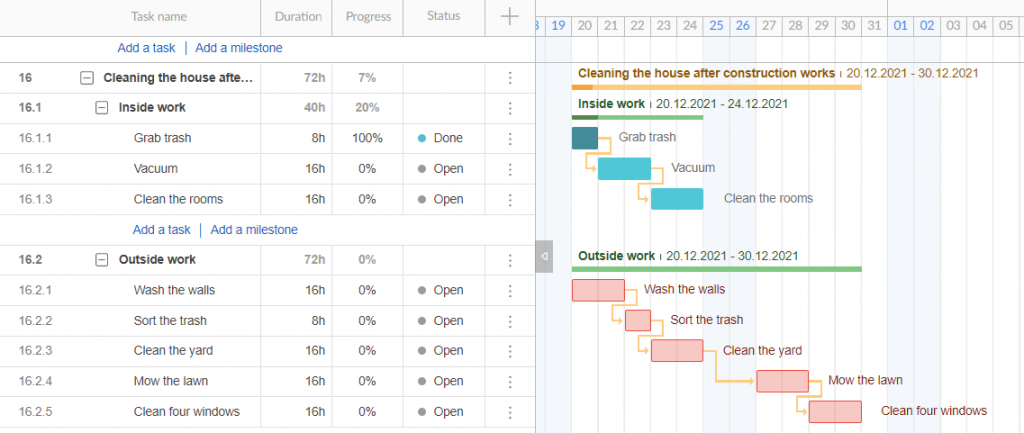
Gantt Chart Example 2
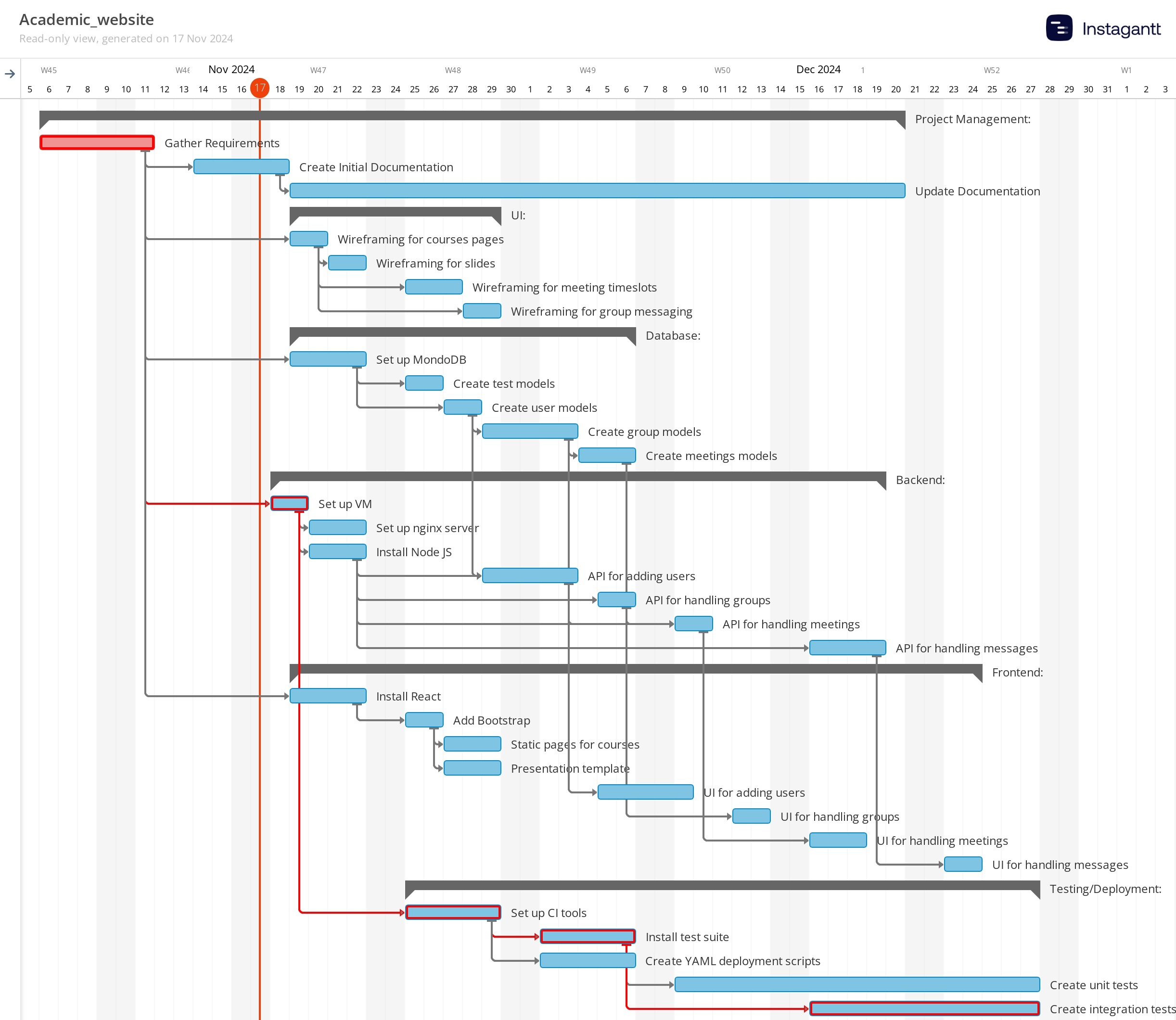
Gantt Chart Example 3
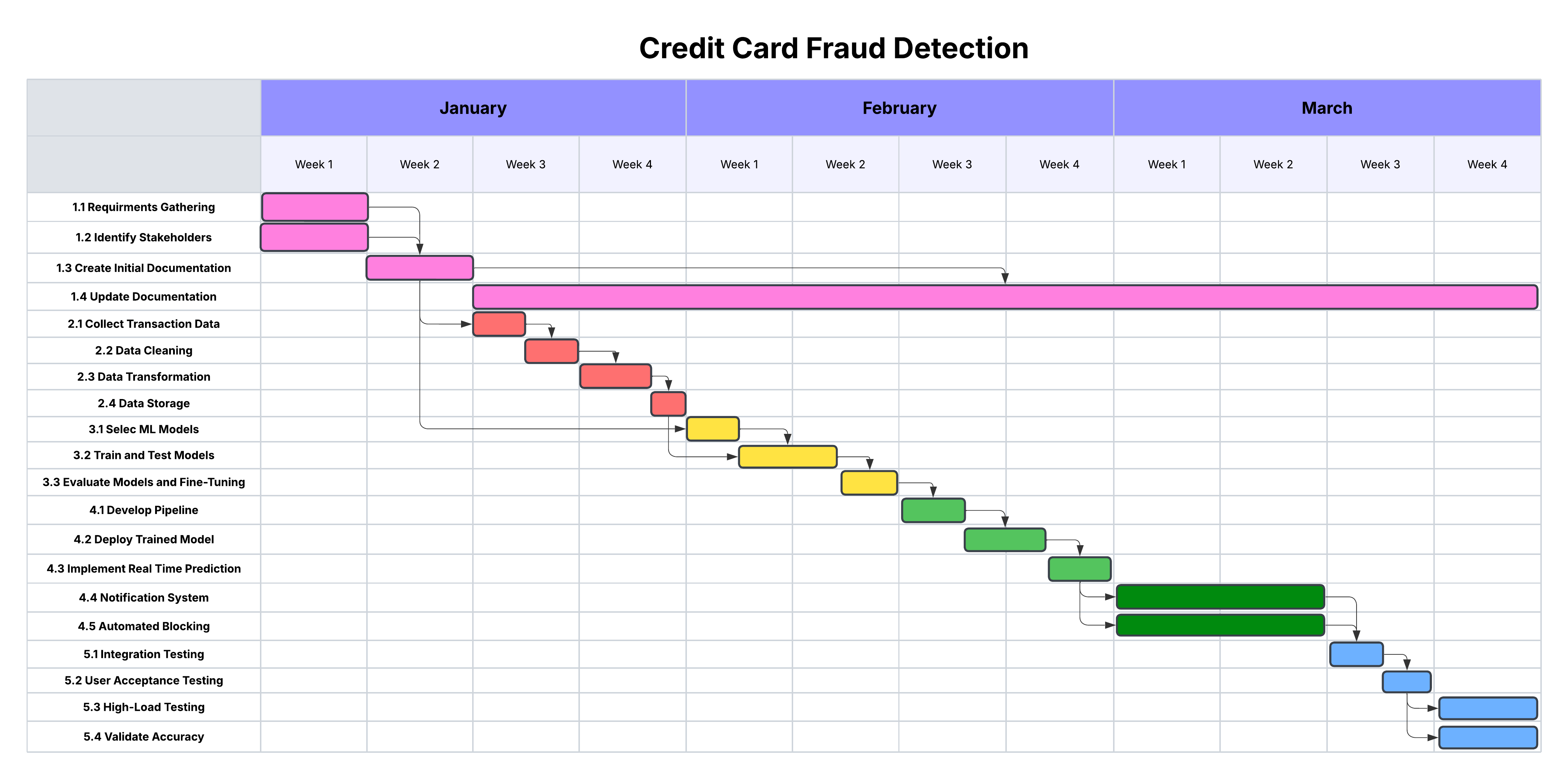
Cost Management
What is Cost?
“Resource sacrificed or foregone to achieve a specific objective ”
“simply put: money”
Cost Management
After estimating scope and timeline, a cost analysis is required to start up a project
Costs come from multiple sources: personnel, equipment, real state, licenses, etc.
In what follows we will cover Cost Estimation Techniques and Budgeting in Scrum
Cost Estimation
Cost Estimation Techniques
Top-down Uses similar projects as basis
Bottom-Up Uses the WBS as a basis
Parametric Uses metrics such as cost of line of code
Estimation Problems
Quick Estimation Rushed to meet deadlines
Lack of Experience Most devs are not accountants
Biases Leading to underestimation
Definitions
Profit revenue - expenditures
ROI ratio by which revenue exceeds investment
Cost Overrun how much actual costs exceed estimates
Budgeting in Scrum
Budgeting in Scrum
The Product Owner is reponsible for budgeting
Two main components:
Personnel costs: team
Fixed costs: hardware, software, infrastructure
Budgeting in Scrum
For personel costs, it is best to get the cost per sprint
Each member has a daily rate and an allocation rate
daily rate × allocation rate = daily burn rate
daily burn rate × number of days = sprint burn rate
Total sprint cost: sum of the cost of all members
Budgeting in Scrum
Let's assume that we have three developers
Each developer has a daily rate (for weekdays), which can be calculated as annual salary/260
Each developer has its own allocation rate between different projects
Each sprint takes two weeks (10 weekdays)
Budgeting in Scrum
| Role | Rate | Allocation | Burn Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product owner | $600 | 50% | $3,000 |
| Dev Team | $400 | 100% | $4,000 |
| Dev Team | $300 | 100% | $3,000 |
| Total | $10,000 |
Budgeting in Scrum
If the project is expected to last for a total of 6 sprints:
Total Personnel cost: 10,000 * 6 = 60,000
If fixed costs are 20,000...
Total Cost: 80,000
Budgeting in Scrum
It is always good to have a 10% - 15% contingency
For the example, this would result in: 80,000 * 10/100 = 8,000 in contigency
Total Cost (including contigency): 88,000
Budget overruns should be reported early
Reading Material
Project Management (Chapter 10 - Blackboard)
Project Management (Chapter 12 - Blackboard - until Managing the Budget)